Flashbots, a leading research group focused on MEV (Maximal Extractable Value), has issued a new warning that spam from MEV bots is quickly becoming the main barrier to blockchain scalability.
In a thesis published this week, Flashbots said that “MEV has become the dominant limit to scaling blockchains,” pointing to rising inefficiencies across Ethereum rollups and Solana.
The group stated that current scaling efforts by major blockchains are being neutralized by increasingly dominant MEV-driven activity.
Flashbots Exposes Scaling Illusion on Rollups
As layer-1 and layer-2 networks race to boost throughput, the report finds that wasteful on-chain activity from MEV bots is consuming a growing share of available capacity.
On Solana, MEV bots are now responsible for 40% of all blockspace. On Ethereum’s OP-Stack rollups like Base and OP Mainnet, spam bots account for over half of all gas usage while paying just a fraction of the network’s fees.
The report noted that between November 2024 and February 2025, Base added 11 million gas units per second of throughput, nearly triple the Ethereum mainnet. However, most of that additional capacity was devoured by bots running repetitive, low-value trades.
This activity creates artificially high fees for users and renders technical scaling efforts less effective. Flashbots introduced a new metric, “effective gas throughput,” to show the difference.
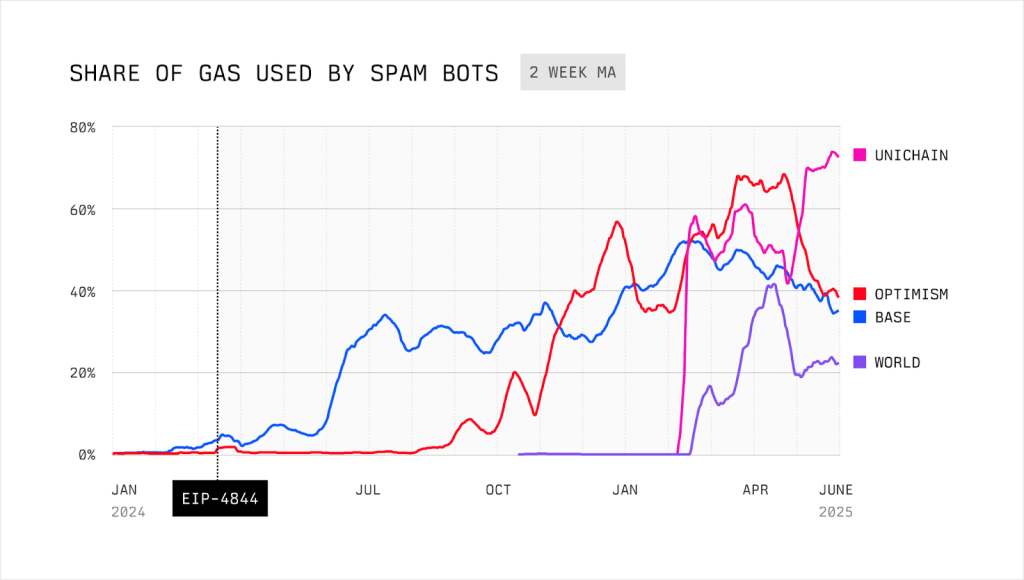
Despite Base increasing its total gas capacity by 11 million gas per second over several months, the throughput available to real users barely changed. Almost all new capacity was eaten up by bots.
The report identified spam as a specific kind of wasteful behavior, mostly DEX queries that never result in token transfers. These could be done off-chain, but instead they clog networks and raise the computational load on nodes.
On Base, bots were responsible for 56% of gas usage and 26% of L1 data availability usage, but paid just 14% of fees.
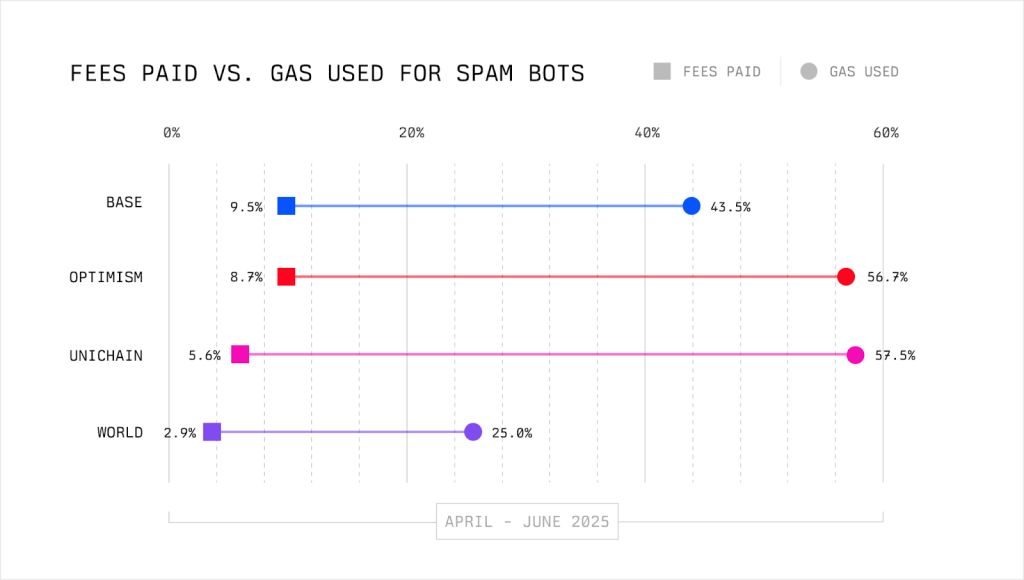
Spam is also driving up user fees. Flashbots explained that despite technical progress in reducing costs on rollups, fees stay artificially high due to bots continuously bidding for blockspace.
“The promise of scaling is to drive fees near zero,” the report stated. “But what we’re seeing is a fee floor created by spam—not user demand.”
The report also showed that this spam is highly concentrated. Just two searchers are behind over 80% of all spam on Base.
According to Flashbots, the structure of the current market makes spam more profitable than participating in a fair auction, leading to inefficient and wasteful outcomes.
“Spam bots are flooding blocks, not to serve users, but to extract MEV,” the report said. “It’s a structural issue, not just a technical one.”
Flashbots Proposes MEV Auction Fix Amid Rising Exploits
Flashbots has proposed a new framework to address growing concerns around MEV exploitation in Ethereum and other blockchain networks. Rather than relying on gas-heavy spam auctions, Flashbots suggests a shift toward explicit MEV auctions, allowing searchers to bid directly for transaction ordering rights.
This, they argue, would reduce network congestion and wasted fees while preserving efficiency for traders and validators.
The organization is also advocating for “programmable privacy,” a model that allows bots to view live blockchain state and plan profitable trades without the ability to front-run users or leak sensitive data.
Flashbots is currently testing this concept using Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs), which allow secure transaction backrunning without the back-run transactions to abuse.
“We’ve proven this on Ethereum L1,” Flashbots wrote in its latest report. “And we’re actively adapting it for L2s.”
The proposal comes at a key time as concerns over MEV-related abuse continue to mount. According to EigenPhi data, more than 33,000 users were victims of sandwich attacks in March 2025, orchestrated by just 101 entities.
These attacks now account for nearly $1 billion in weekly trading volume on Ethereum-based DEXs.
In 2023, a single MEV searcher earned over $1 million in one day using sandwich attacks on Ethereum. On that day alone, the address accounted for 7% of total gas usage across the network. The same operator continued to profit into 2024 with improved strategies.
The issue isn’t limited to Ethereum. On Solana, a well-known MEV bot named “arsc” exploited users through similar tactics, generating around $30 million in just two months.
MEV allows validators to extract profits by reordering or inserting transactions. While it can boost DeFi efficiency, it also drives up fees and undermines fairness, especially for beginners unfamiliar with blockchain mechanics.
Critics warn that unchecked MEV practices could deter user adoption and erode trust in decentralized finance.